Track Cryptocurrency : Real-Time Insights with Dynamic Light and Dark Mode Dashboards in Power BI
- Tanya Sharma
- Aug 5, 2024
- 5 min read
How to Import Cryptocurrency Data Using Python: A Step-by-Step Guide
Are you looking to integrate cryptocurrency data into your analysis?
This blog post explores using Python scripts to automate the import process, making it easier to track and analyse crypto market trends.
Step 1: Convert ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ to UNIX Timestamp
Yahoo Finance uses UNIX timestamps to specify date ranges for historical data. We'll start by converting a date in the format `YYYY-MM-DD` to a UNIX timestamp.
import time
def date_to_unix(date_str):
return
int(time.mktime(time.strptime(date_str, "%Y-%m-%d")))# Example
start_date = '2023-07-01'
unix_start_date = date_to_unix(start_date)
print(f"Start Date: {start_date} -> UNIX Timestamp: {unix_start_date}")
Output:
Start Date: 2023-07-01 -> UNIX Timestamp: 1688169600Step 2: Get the Current Date in ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ Format
Next, we fetch the current date to use it as the end date for fetching historical crypto data.
from datetime import datetime
current_date = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
unix_current_date = date_to_unix(current_date)
print(f"Current Date: {current_date} -> UNIX Timestamp: {unix_current_date}")Output:
Current Date: 2024-07-28 -> UNIX Timestamp: 1722124800
Step 3: Read the CSV File to Get the List of Crypto Symbols
We store the crypto symbols (trackers) in a CSV file, which we'll read into a data frame.
import pandas as pd
file_path = 'path/to/your/csvfile.csv'
symbols_df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
trackers = symbols_df['Symbol'].tolist()
print("Crypto Symbols:")
print(trackers)Output:
Crypto Symbols:
['BTC-USD', 'ETH-USD', 'XRP-USD', 'LTC-USD']Step 4: Initialize a List to Hold All Data
We'll create an empty list to store the DataFrames for each crypto's historical data.
data_frames = []Step 5: Fetch Data from Yahoo Finance
Now, we'll loop through each crypto symbol, construct the URL for Yahoo Finance, fetch the historical data, and store it in a data frame.
period1 = date_to_unix(start_date)
period2 = date_to_unix(current_date)for tracker in trackers:
url = f'https://query1.finance.yahoo.com/v7/finance/download/{tracker}?period1={period1}&period2={period2}&interval=1d&events=history&includeAdjustedClose=true'
try:
df = pd.read_csv(url)
df['Symbol'] = tracker
data_frames.append(df)
print(f"Data for {tracker} downloaded successfully.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to download data for {tracker}: {e}")Output:
Data for BTC-USD downloaded successfully.
Data for ETH-USD downloaded successfully.
Data for XRP-USD downloaded successfully.
Data for LTC-USD downloaded successfully.Step 6: Concatenate All DataFrames into a Single DataFrame
Once all data has been fetched and stored in individual DataFrames, we concatenate them into a single DataFrame.
combined_data = pd.concat(data_frames, ignore_index=True)
combined_data = combined_data[['Symbol', 'Date', 'Open', 'High', 'Low', 'Close', 'Adj Close', 'Volume']]
print(combined_data.head())Output:
Symbol Date Open High Low Close Adj Close Volume
0 BTC-USD 2023-07-01 192.020004 194.610001 191.889999 192.460007 191.362930 59021500
1 BTC-USD 2023-07-02 190.850006 193.160004 190.179993 192.800003 191.700000 48655000
2 BTC-USD 2023-07-03 192.470001 193.490005 192.100006 193.240005 192.150009 37538000
3 BTC-USD 2023-07-04 193.169998 194.479996 192.479996 193.149994 192.060000 50777000
4 BTC-USD 2023-07-05 192.800003 195.029999 192.600006 194.169998 193.070000 55548000Full Script after merging above code:
import pandas as pd
import time
from datetime import datetime
def date_to_unix(date_str):
return int(time.mktime(time.strptime(date_str, "%Y-%m-%d")))
current_date = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
start_date = '2023-07-01'
period1 = date_to_unix(start_date)
period2 = date_to_unix(current_date)
file_path = 'path/to/your/csvfile.csv'
symbols_df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
trackers = symbols_df['Symbol'].tolist()
data_frames = []
for tracker in trackers:
url = f'https://query1.finance.yahoo.com/v7/finance/download/{tracker}?period1={period1}&period2={period2}&interval=1d&events=history&includeAdjustedClose=true'
try:
df = pd.read_csv(url)
df['Symbol'] = tracker
data_frames.append(df)
print(f"Data for {tracker} downloaded successfully.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to download data for {tracker}: {e}")
combined_data = pd.concat(data_frames, ignore_index=True)
combined_data = combined_data[['Symbol', 'Date', 'Open', 'High', 'Low', 'Close', 'Adj Close', 'Volume']]
print(combined_data.head())Why Use a Date Time Period Slicer?
A date-time period slicer offers several benefits:
Dynamic Time Periods: Allows users to analyze data across various time frames without manually selecting date ranges.
Improved Insights: Facilitates quick comparison of different periods, enabling better decision-making.
Ease of Use: Simplifies data interaction for end-users, enhancing the overall experience in Power BI dashboards.
Custom Reporting: Tailors reports to specific business needs, such as comparing recent performance to historical trends.
Setting Up Your Power BI Environment
Before we begin, ensure that you have the following:
Power BI Desktop: Download and install it from the official Power BI website.
Sample Dataset: Use a stock data sample that includes a Date column to apply the slicer.
Creating the Date Category DAX Formula
To create an advanced date time period slicer, write a DAX formula that categorizes each date into a specific time period. Here’s the process:
Step 1: Open Power BI Desktop
Launch Power BI Desktop and load your dataset. Ensure your dataset contains a Date column for the slicer.
Step 2: Create a New Column in Your Data Model
Go to the “Data” view.
Select the table containing your date column (e.g., Stocks Data).
Click on “New Column” in the ribbon.
Enter the following DAX formula:
DAX
Date Category =
VAR TodayDate = TODAY()
VAR StartOfYears = DATE(YEAR(TodayDate), 1, 1)
VAR FiveDaysAgo = TodayDate - 7
VAR ThreeMonthsAgo = EOMONTH(TodayDate, -3) + 1
VAR SixMonthsAgo = EOMONTH(TodayDate, -6) + 1
VAR OneYearAgo = EOMONTH(TodayDate, -12) + 1
VAR FiveYearsAgo = EOMONTH(TodayDate, -60) + 1
VAR MaxDate = CALCULATE(MAX('Stocks Data'[Date]), ALL('Stocks Data'[Date]))
RETURN
SWITCH(
TRUE(),
'Stocks Data'[Date] > TodayDate, "Future",
'Stocks Data'[Date] >= TodayDate, "Today",
'Stocks Data'[Date] >= FiveDaysAgo && 'Stocks Data'[Date] < TodayDate, "5D",
'Stocks Data'[Date] >= ThreeMonthsAgo && 'Stocks Data'[Date] < TodayDate, "3M",
'Stocks Data'[Date] >= SixMonthsAgo && 'Stocks Data'[Date] < ThreeMonthsAgo, "6M",
'Stocks Data'[Date] >= StartOfYears && 'Stocks Data'[Date] < TodayDate, "YTD",
'Stocks Data'[Date] >= OneYearAgo && 'Stocks Data'[Date] < StartOfYears, "1Y",
'Stocks Data'[Date] >= FiveYearsAgo && 'Stocks Data'[Date] < OneYearAgo, "5Y",
'Stocks Data'[Date] >= MaxDate && 'Stocks Data'[Date] < FiveYearsAgo, "Max",
"Older"
)Explanation of the DAX Formula
The provided DAX formula categorizes dates into various time periods. Let's break down each part of the formula:
Variable Definitions
1. TodayDate:
VAR TodayDate = TODAY()
Retrieves the current date using the `TODAY()` function.
2. StartOfYears:
VAR StartOfYears = DATE(YEAR(TodayDate), 1, 1)
Calculates the start of the current year by setting the month and day to January 1st of the current year.
3. FiveDaysAgo:
VAR FiveDaysAgo = TodayDate - 7
Computes the date five days prior to today.
4. ThreeMonthsAgo:
VAR ThreeMonthsAgo = EOMONTH(TodayDate, -3) + 1
Determines the date three months ago, set to the first day of the month.
5. SixMonthsAgo:
VAR SixMonthsAgo = EOMONTH(TodayDate, -6) + 1
Identifies the date six months ago, set to the first day of the month.
6. OneYearAgo:
VAR OneYearAgo = EOMONTH(TodayDate, -12) + 1
Finds the date one year ago, set to the first day of the month.
7. FiveYearsAgo:
VAR FiveYearsAgo = EOMONTH(TodayDate, -60) + 1
Establishes the date five years ago, set to the first day of the month.
8. MaxDate:
VAR MaxDate = CALCULATE(MAX('Stocks Data'[Date]), ALL('Stocks Data'[Date]))
Retrieves the maximum date in the dataset to categorize any dates older than five years.
Visualizing Cryptocurrency Data in Power BI
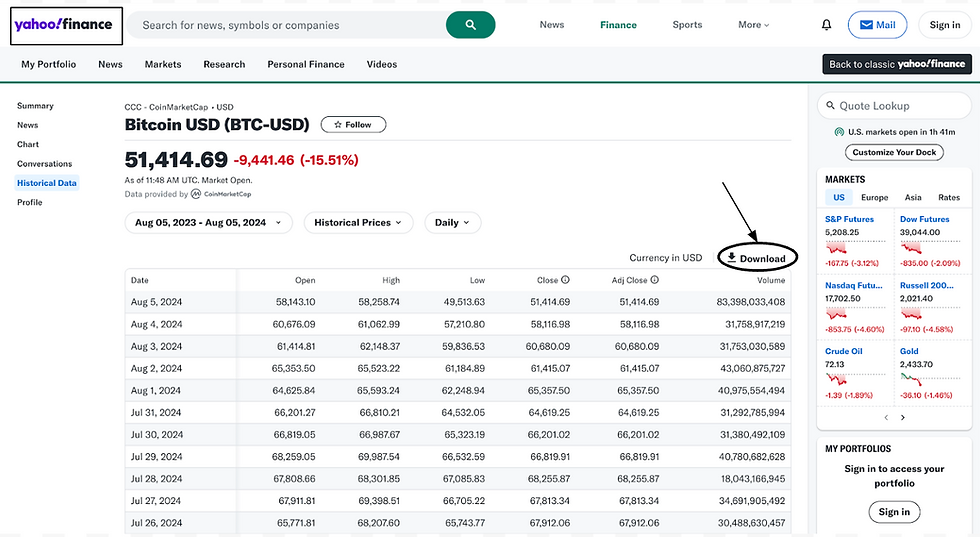
One of the standout features of our Power BI dashboard is the dynamic visualization using light and dark modes, achieved through innovative use of layers and shapes. Here are the key points:
Dynamic Visual Modes:
Utilizes both light and dark modes for enhanced user experience.

Achieved through innovative use of layers and shapes.
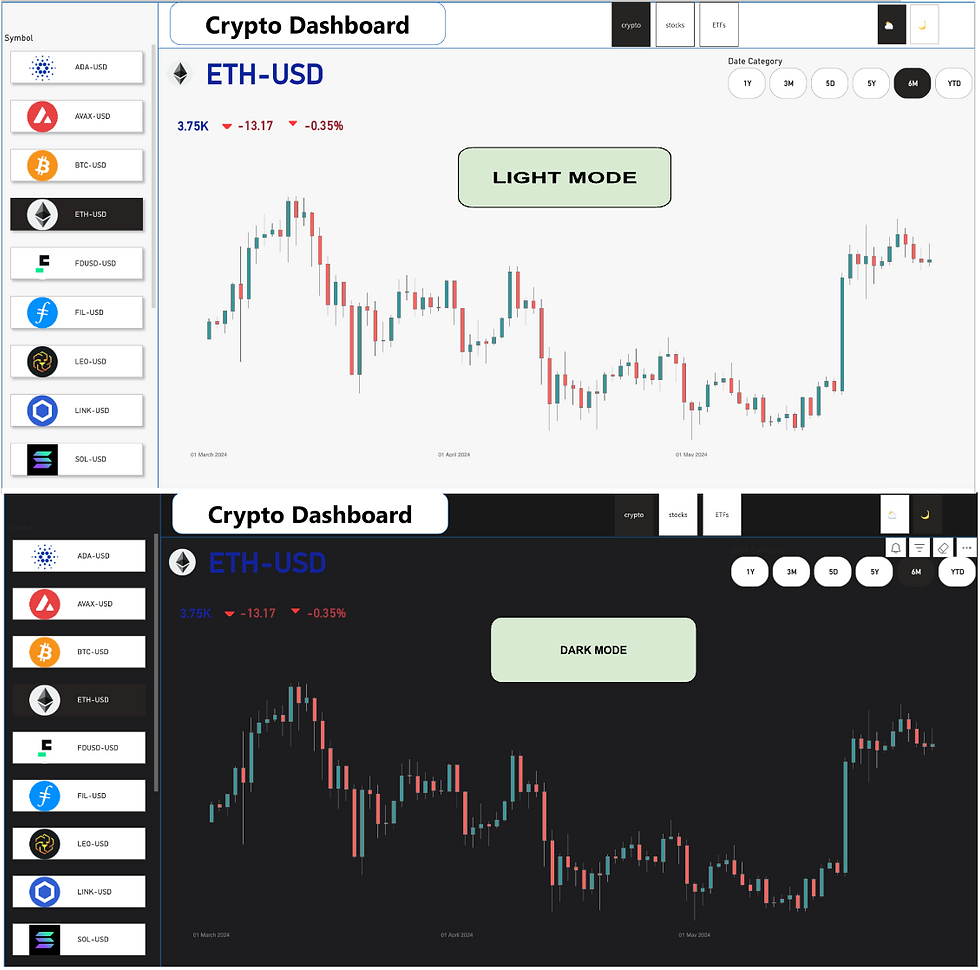
Real-Time Data Updates:
Displays daily profit and loss for selected cryptocurrencies.
Requires an active internet connection for live data updates.

Advanced Date Category Slicer:
Offers various time frames: 3 days, 5 days, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year.
Allows users to analyze trends and patterns over different periods.

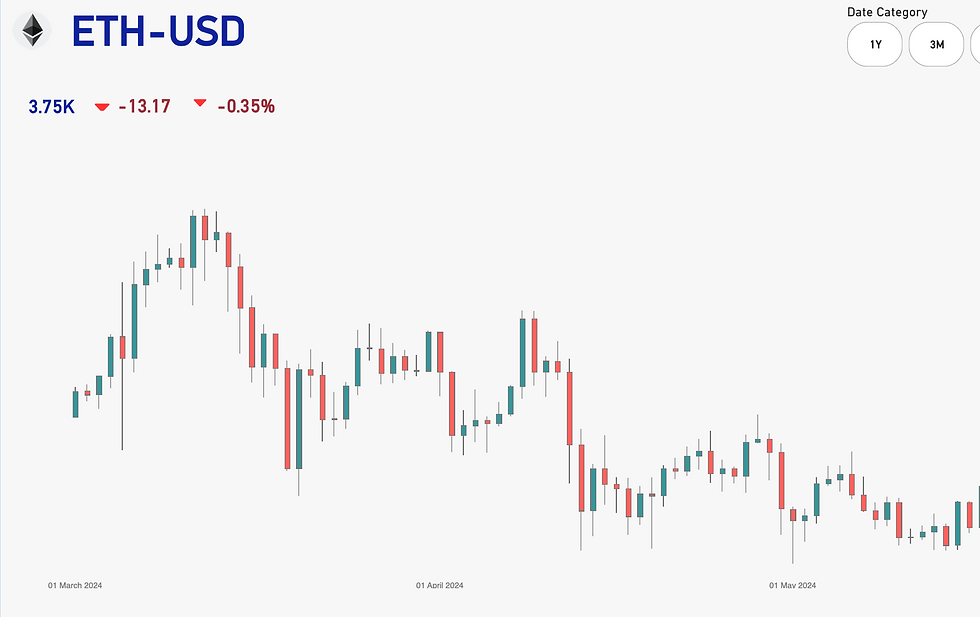
Candlestick Chart Visualization:
Used to display the value fluctuations of the selected cryptocurrency.
Showcases open, high, low, and close values for comprehensive market behaviuor insights.
Interactive Slicer:
Users can select a cryptocurrency from the slicer to view live data updates.
Provides up-to-the-minute information for informed decision-making.

Comprehensive Tabs:
Includes three tabs for a broader range of data: Stocks, ETFs, and Cryptocurrencies.
Ensures a holistic approach to market analysis.

This combination of real-time data, dynamic visual modes, and comprehensive time period analysis makes the Power BI dashboard a powerful tool for monitoring and understanding the ever-changing cryptocurrency market.
Link of Dashboard - link
Resources from The Developer

Comments